
ISUZU MOTORS Co. Ltd. and EUGLENA Co. Ltd. aiming at practical use of the next generation “Midorimushi” microalgae-derived bio-fuel by 2018 with the “DeuSEL” project
(21/07/16). ISUZU MOTORS Co. Ltd. and EUGLENA Co. Ltd. are joining efforts in the joint projectDeuSEL [1] aiming at the practical use of the next generation bio-fuel in 2018. The project is divided by 2 main different roles depending of the Company, and various stages (Table 1):
 |
 |
Table 1. Stages of the “DeuSEL” project.
The project consists of a series of tests using the Midorimushi bio-fuel on the DeuSEL bus. To date, the project passed successfully a two-year experiment with a mileage of over 40,000 km. DeuSEL can use the existing diesel infrastructures such as (1) storage tanks, (2) the regular service stations for diesel vehicles and (3) trucks for transportation of fuel.
By using the Midorimushi bio-fuel there are 4 main assets; (1) it helps to tackle the current high dependence on fossil oil imports by enhancing the production of local microalgae-based bio-combustibles, (2) the CO2 emissions are significantly reduced when compared with conventional fuels [2-3], the energy security is improved [4] and it is shaped a sustainable business model through microalgae as it is depicted in the next carbon cycle (Figure 1).
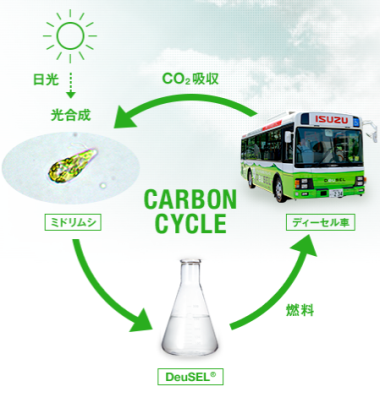
Figure 1. The carbon cycle of the project.
Furthermore, the DeuSEL project created an interactive “HaKoBu” [5] community web in order to (1) enhance the awareness among the potential future customers about the importance of using the Midorimushi bio-fuel and (2) for detailing how the proposed carbon cycle works, as 2 keys for success.
EU-Japan Centre Comments:
Sources:
Based on an interview with Mr. Kobayashi (ISUZU MOTORS Co. Ltd.), person in charge of the DeuSEL project, on 21/07/2016. Full transcript can be provided.
[1] DeuSEL. Midorimushi bio-fuel. Available online: http://www.deusel.jp (accessed 22 July 2016) (only available in Japanese)
[2] Algae Biofuel Emits at Least 50% Less Carbon than Petroleum Fuels. Available online: http://inhabitat.com/algae-biofuel-emits-more-than-half-the-carbon-emissions-of-petroleum/ (accessed 22 July 2016)
[3] ALGAE BIOFUEL CAN CUT CO2 EMISSIONS BY UP TO 68 PERCENT COMPARED TO PETROLEUM FUELS FINDS NEW PEER REVIEWED STUDY. Available online: http://algaebiomass.org/algae-biofuel-can-cut-co2-emissions-by-more-than-50-compared-to-petroleum-fuels-finds-new-peer-reviewed-study/ (accessed 22 July 2016)
[4] Biofuels improve energy security. Available online: http://bioenergy.novozymes.com/en/learn-more/publications/Documents/Biofuels_improve_energy_security.pdf (accessed 22 July 2016)
[5] HaKoBu web site. Available online: http://www.i-hakobu.jp/ (accessed 22 July 2016)
Prepared by Manuel Herrador, Minerva Research Fellow, EU-Japan Centre for Industrial Cooperation.
The EU-Japan Centre currently produces 5 newsletters :










Joint venture established in 1987 by the European Commission (DG GROW) and the Japanese Government (METI) for promoting all forms of industrial, trade and investment cooperation between the EU and Japan.
The EU-Japan Centre’s activities are subject to the allocation of a Grant Agreement by the European Commission for 2024-2026

